SoftSwitch
Launched more than ten years ago, SipPulse SoftSwitch is a family of high-performance and robust products, aimed at the telephone operator market with STFC grant, for wholesale operators that need a large volume of calls and resilience and for Contact Centers that need to add routing, pricing, recording and analytics capabilities to their operations.

Target Markets
The SipPulse softswitch targets the markets below and custom products have been created for each segment. Segments have different forms of licensing and unique features.
Wholesale telephone operators, PCRT-SCM product
Telephone operators with STFC grant, PCRT-STFC product
Contact Center companies, PCRT-CRT product
Ways to apply the softswitch
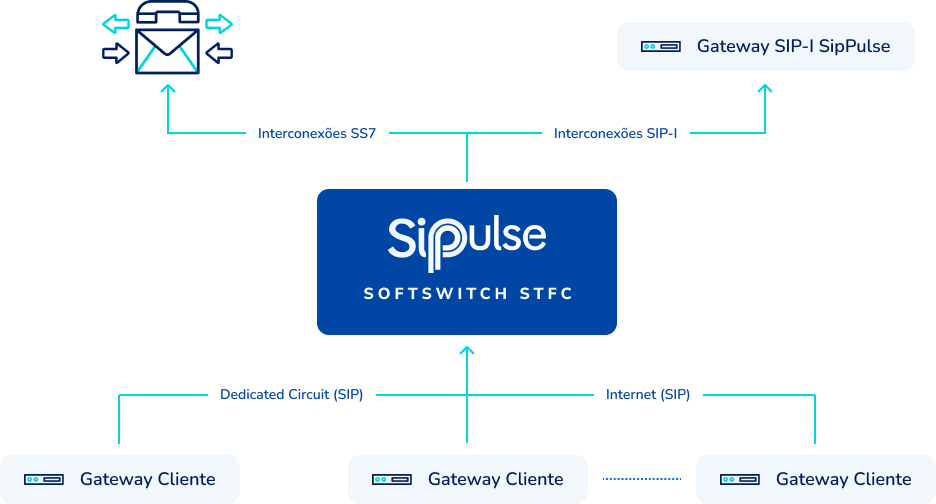
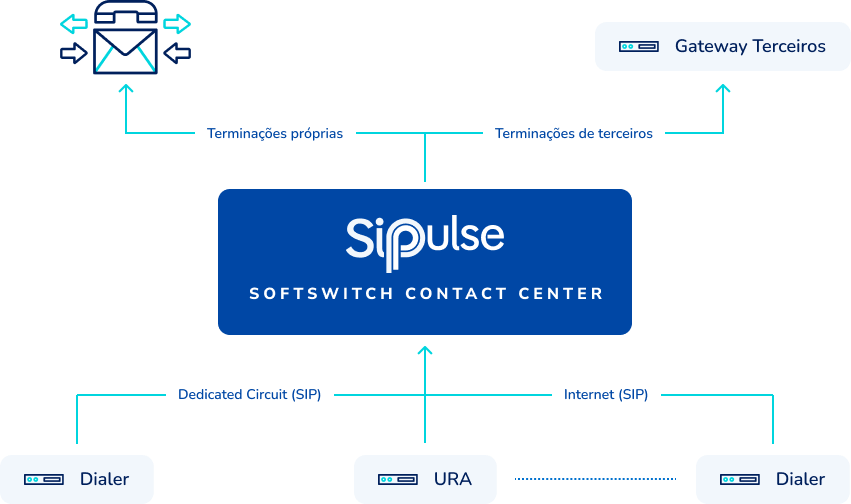
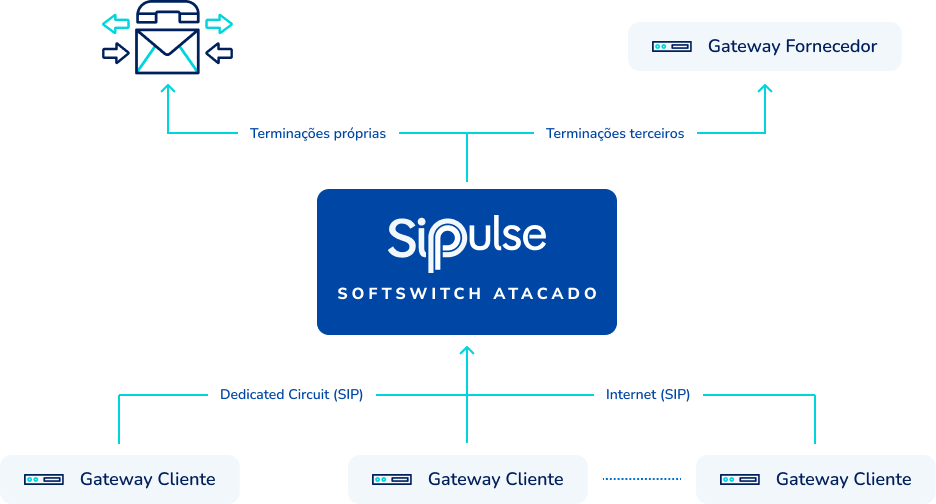
Understand the benefits of this solution:
- Local or geographic redundancy
- Easily scalable by adding new servers
- High call and billing performance, up to 1000 CAPS (call attempts per second)
- Resilience, in-memory operation allows it to survive even database crashes for up to 7 days
- Open architecture with available APIs
- 24/7 Support
- Unlimited balanced recording capability
- Simplified configuration through intelligent routing with portability and area matrix
- Simplified DETRAF configuration through ABR Annex 5 load
- Full control of gateways and transfers for maximum efficiency
- Real-time operation dashboard with activation and deactivation control of gateways and clients
- Fraud security through advanced detection, quotas and limits
SoftSwitch screenshots
SipPulse's SoftSwitch is currently installed in more than 200 operators and Contact Centers
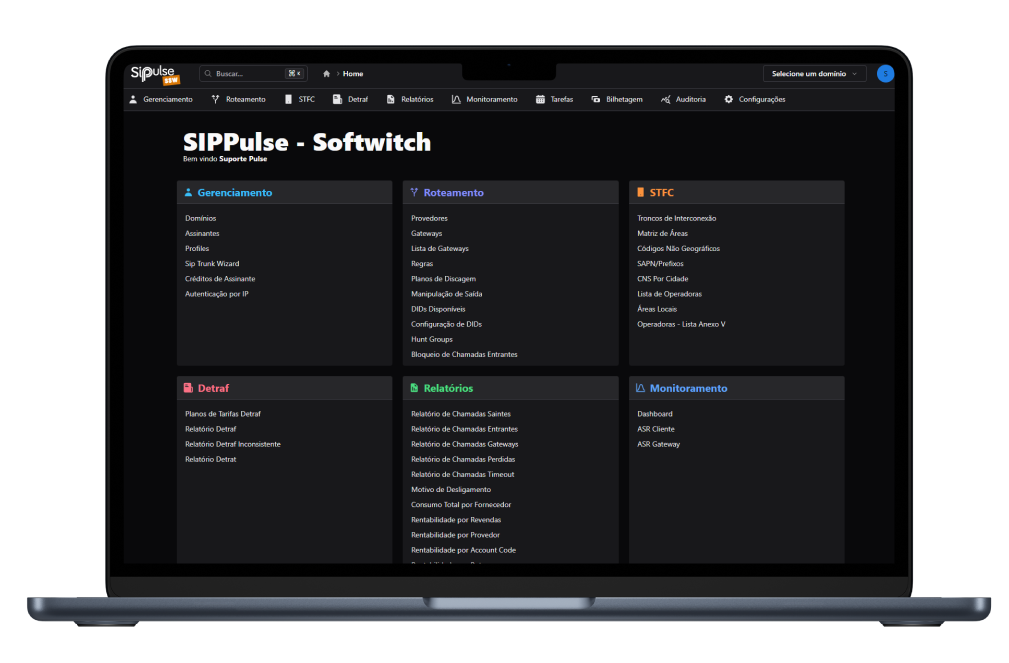
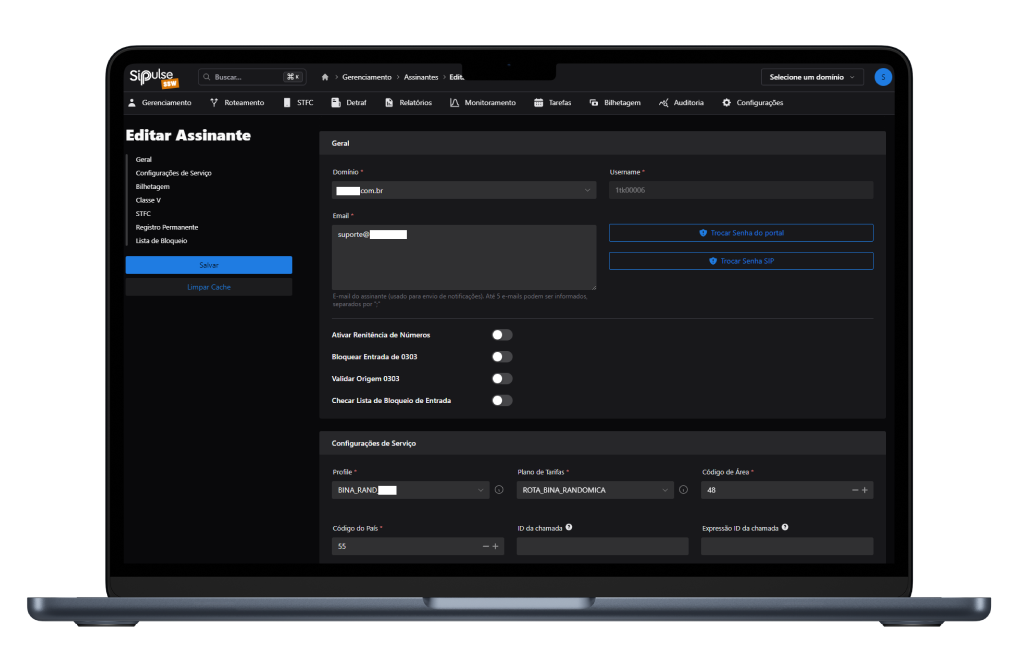
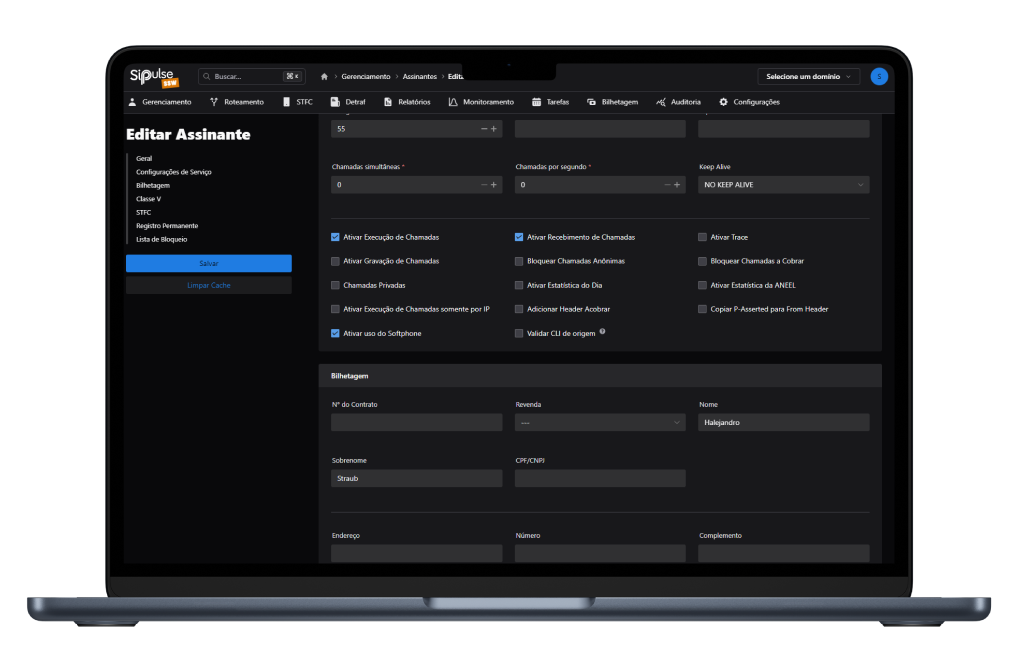
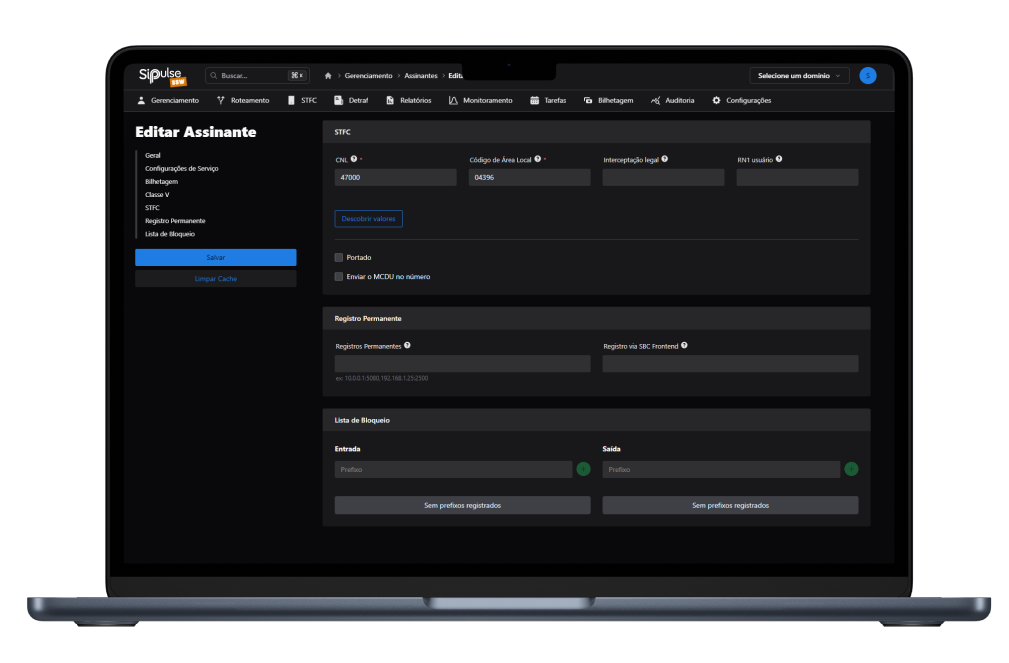
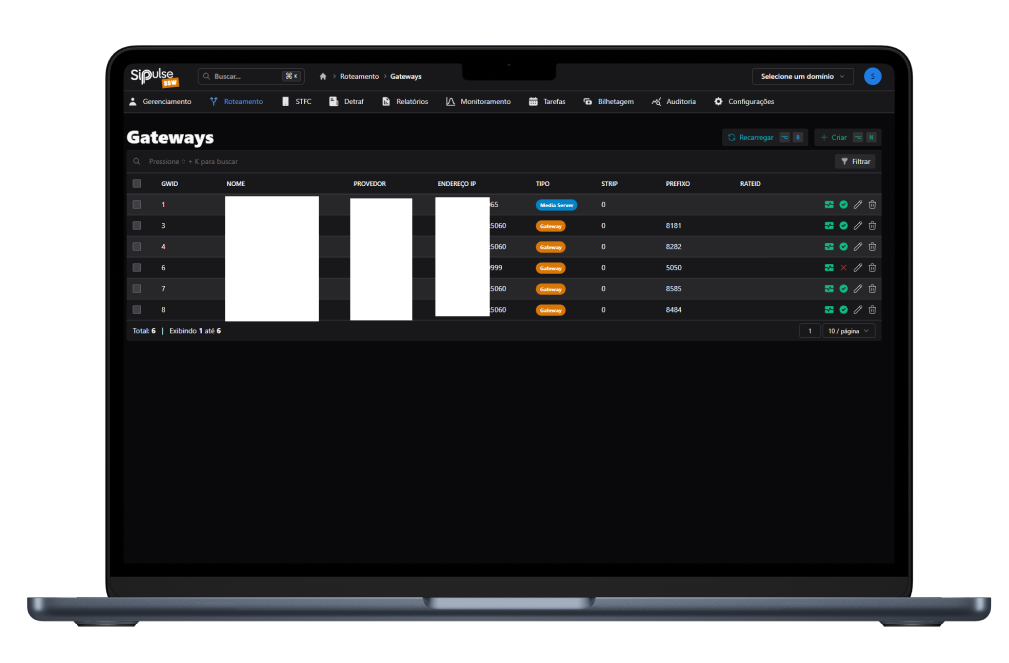
Important SoftSwitch Features
Operation in SIP Proxy and B2BUA Mode
UDP, TCP, TLS, WSS protocols
Topology Hiding
Authentication by IP, Password, IP+TechPrefix, IP+ANI, IP+CLI
Protection against SQL Injection, Anti-Fraud
Serial, balanced, cost and quality routing
STFC automatic routing / Portability
Offline operation without database
Anatel / Aneel reports
Support for collect calls
Prepaid and postpaid pricing
Detraf Generation
Real Time Monitoring
Protection against SQL Injection, Anti-Fraud
Serial, balanced, cost and quality routing
depositions
Who trusts us


softswitch
Ordering information
Model
On-Premise – With hardware installed in your Datacenter
Cloud – Hosted in a TIER3 AWS, AZURE or ORACLE datacenter
Type
SSW-STFC – STFC Operators – License per user and DID
SSW-CRT – SCM Operators – Simultaneous call license
SSW – CC – Contact Center License per simultaneous call
Model
Monthly signature
Indefinite license